Water is the essence of life, and it’s no surprise that we rely on well pumps to access this precious resource from underground sources. These pumps come in all shapes and sizes, but the 3/4 horsepower well pump is one of the most common types you’ll encounter. If you’re a homeowner with a well system or considering installing one, then you might be wondering how much power this pump consumes. That’s where we come in. In this blog post, we’ll dive deep into the question that has been on many homeowners’ minds: “How many amps does a 3/4 hp well pump draw?”
Understanding your well pump’s power consumption is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it can help you determine the size of generator or inverter needed to keep your pump running during power outages. Secondly, it can help you identify whether your pump is running efficiently or consuming too much power, leading to a spike in energy bills. In this article, we’ll answer this critical question by breaking down the key concepts behind well pumps, horsepower, and amperage.
But wait, there’s more. We’ll also discuss what factors can impact your well pump’s power consumption and provide some practical tips to help reduce your energy bills. From understanding motor efficiency to optimizing water usage, we’ve got you covered.
So, let’s get started on our journey to demystify the world of 3/4 horsepower well pumps and their electrical needs. Get ready to learn something new and useful that will benefit both you and our planet.
What is a Well Pump?
Contents

Well, wonder no more. A well pump is a vital device that extracts water from an underground well. It’s usually installed in the well casing and works by creating a vacuum that pulls water up from the ground and into a storage tank or directly into a home’s plumbing system.
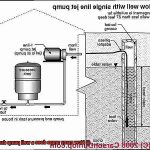
There are two main types of well pumps: submersible pumps and jet pumps. Submersible pumps are perfect for deeper wells because they are designed to be completely submerged in water. On the other hand, jet pumps are installed above ground and use suction to draw water up from shallower wells.
If you live in a rural area or on a farm, well pumps are essential for your daily activities such as drinking, irrigation, and other purposes. These devices come in various sizes and capacities, ranging from small 1/3 horsepower pumps for residential use to large industrial-grade pumps with horsepower ratings of 50 or more.
When choosing a well pump, it’s important to consider several factors such as the depth of the well, the volume of water needed, and the available power source. It’s also crucial to choose a pump that is energy-efficient and reliable, easy to maintain, and repairable.
Let’s talk about electrical requirements. The number of amps a 3/4 hp well pump draws depends on several factors such as the voltage of the pump. Most well pumps have either 115 or 230 volts.
For a 115-volt pump, a 3/4 hp motor will draw around 12-13 amps while running. However, during start-up, the motor may draw up to 20 amps for a brief moment. It’s crucial to ensure that your electrical system can handle this momentary surge in power without tripping any breakers or causing damage.
For a 230-volt model, the amperage is less overall. A 3/4 hp motor running at 230 volts will typically draw around 6-7 amps while in operation. During start-up, the amperage may rise to around 12-15 amps.
However, it’s essential to note that these are just estimates, and the actual amperage may vary depending on several factors such as the age and condition of the pump or additional components in the system.
Factors Affecting Amperage of a 3/4 HP Well Pump
There are several factors that come into play, but the good news is that understanding these factors can help you optimize your pump’s performance and efficiency while minimizing your energy costs.
First and foremost, the size and depth of your well will have a significant impact on how many amps your pump will draw. The larger your well and the greater its depth, the more power your pump will need to move water up. This increased power demand translates to higher amperage draw. If you have a deep well, you may need to invest in a more powerful pump to ensure that it can handle the job without drawing too many amps.
The type of motor in your well pump also plays a critical role in determining its amperage. Different motor types have varying efficiencies and power requirements, affecting the number of amps they draw. For instance, a single-phase motor may draw more amps than a three-phase motor with the same horsepower rating. To minimize your energy costs, consider investing in a well pump with an efficient motor.
The condition of your well pump and its components is another critical factor to consider. If your well pump is aging or has worn-out parts, it may require more power to operate, increasing its amperage draw. Additionally, if the electrical wiring or circuitry powering your well pump is not up to code or is damaged, this can affect its amperage draw. Regular maintenance and inspection can help keep your well pump running efficiently.
Finally, environmental factors such as temperature and humidity can impact how many amps your 3/4 HP well pump draws. In colder temperatures, for instance, the viscosity of the water in the well may increase, making it harder for the pump to move water and increasing its power requirements.
If you live in an area with extreme temperatures or high humidity levels, consider taking extra steps to ensure that your well pump can handle the job without drawing too many amps.
115-Volt Pumps
Look no further than the 115-volt pump. These pumps are designed to operate on a standard household electrical circuit, making them convenient for homeowners who want a reliable water source without any special wiring.
If you’re wondering about power consumption, a 115-volt pump with a 3/4 horsepower motor will typically draw around 9-10 amps of current when operating at full capacity. However, keep in mind that this may vary depending on factors like the age and condition of the pump, as well as the depth and diameter of your well.
While these pumps are perfect for shallow wells or water sources that don’t require a lot of water flow, they may not be suitable for larger or deeper wells that require higher flow rates. In these cases, we recommend using a higher voltage pump to provide sufficient water pressure and volume.
It’s crucial to understand the amperage requirements of your well pump to ensure proper installation and operation. You’ll also want to avoid potential electrical hazards by consulting with a licensed electrician or pump specialist if you have any questions or concerns about your specific well pump setup.
230-Volt Pumps
If so, one of the most critical factors to consider is the voltage of the pump. In this section, we’ll delve into 230-volt pumps and why they’re an excellent choice for many homeowners.
It’s essential to note that a 230-volt pump requires a dedicated circuit with a double-pole breaker. Your home’s electrical wiring must be able to handle this type of voltage before purchasing a 230-volt pump. This ensures safe and optimal performance of the pump.
When it comes to amperage, a 3/4 hp well pump operating at 230 volts draws around 6 amps. However, this may vary depending on the well’s size and depth, as well as the brand and model of pump you’re using. Therefore, it’s best to consult the manufacturer’s specifications to determine your particular pump’s amperage requirements.
One of the most significant advantages of 230-volt pumps is their efficiency. Pumps that run at higher voltages tend to be more efficient than those at lower voltages. This means they require less energy to operate, which can lead to substantial savings on your utility bills over time.
Other Considerations
Other factors also play a crucial role in determining the amp draw of your pump.
The type of motor used in your pump is a significant consideration. Above-ground pumps typically use induction motors, which are reliable and highly efficient. These motors have a lower current draw when starting up but require more amps when running at full capacity. In contrast, submersible motors used in below-ground pumps require a higher starting current. Once they’re running, their amp draw decreases.
Voltage is another key consideration when it comes to determining amp draw. Most well pumps operate on either 120 or 240 volts. Higher voltage levels result in lower amp draws, while lower voltage levels result in higher amp draws.
It’s also essential to consider any additional components attached to your well pump. Components such as pressure switches and control boxes can impact the amp draw of your system. Neglecting these components when calculating your total amp draw can lead to inefficient operation and potential equipment damage.
Safety Tips for Working with Well Pumps
Working with well pumps can be a challenging task that requires careful attention to safety. As an expert in the field, I know how important it is to prioritize safety while working with well pumps. Here are some essential safety tips to keep in mind:
Turn off the power
Before getting started on any work involving a well pump, make sure to turn off the power supply. This can be done by switching off the circuit breaker or disconnecting the power at the control box. By doing this, you can protect yourself from electric shocks and other accidents.
Wear protective gear
It is crucial to wear protective gear when working on a well pump. This includes gloves, eye protection, and appropriate clothing. Protective gear shields you from potential hazards that may arise when working on the well pump.
Use proper tools
Always use the right tools for the job. Using makeshift tools can lead to accidents and injuries. Ensure that you have all the necessary tools and equipment before commencing any work.
Be aware of hazards
When working with well pumps, there are many hazards that can arise. These may include electrical shocks, exposure to chemicals, and physical injuries. Be mindful of these risks and take preventive measures to ensure your safety.
Follow manufacturer instructions
Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions when installing, maintaining, or repairing a well pump. This ensures that you complete the job correctly and safely without any errors.
Keep the area clean
Make sure to keep the area around the well pump clean and free from debris. This helps prevent accidents and injuries while working on the well pump.
Seek professional help if needed
If you are unsure of what to do or not comfortable working on a well pump, seek professional help. It is always better to be safe than sorry.
WgIA19fmvV8″ >
Conclusion
In conclusion, grasping the amperage requirements of a 3/4 horsepower well pump is crucial for homeowners who rely on wells to access water. Knowing the amperage draw of your pump can help you determine the appropriate size of generator or inverter required during power outages. It can also help you identify whether your pump is running efficiently or consuming too much power, causing an unwelcome spike in energy bills.
The amperage draw of a 3/4 hp well pump hinges on several factors such as voltage, well depth and size, motor type, and the condition of the pump and its components. Therefore, it’s essential to choose an energy-efficient and reliable well pump that is easy to maintain and repair.
Regular maintenance and inspection can keep your well pump functioning optimally. However, safety should always come first when working with well pumps. Before conducting any work involving a well pump, turn off the power supply, wear protective gear, use proper tools, be aware of hazards, follow manufacturer instructions, keep the area clean, and seek professional assistance if necessary.
By understanding these key concepts behind well pumps’ horsepower and amperage draw while following these tips, homeowners can optimize their wells’ efficiency while minimizing energy costs.