Are you curious about the energy consumption of LED light bulbs? These innovative bulbs have transformed lighting technology with their impressive energy efficiency and versatility. Unlike traditional incandescent bulbs that waste a significant amount of energy generating heat, LEDs use less power to produce brighter light. But, have you ever wondered how many amps an LED bulb draws?
Before we dive into the specifics, let’s review some electrical circuit basics. An amp is a unit of electric current that flows through a conductor, determining the rate of energy flow. In simpler terms, it indicates how quickly electricity moves in a circuit. The amperage of an LED bulb depends on its wattage and voltage rating. LEDs consume less wattage than other bulbs and can operate at lower voltages.
In this blog post, we will explore the concept of LED bulb amperage and how to calculate it accurately. We will also discuss various types of LED bulbs available in the market and their power ratings. Furthermore, we will explain why considering an LED bulb’s amperage is crucial when selecting a compatible power source such as batteries or power supply units.
Ultimately, understanding how many amps an LED bulb draws is essential for calculating its power consumption accurately, ensuring optimal electrical performance and extending its lifespan. So let’s jump right in.
What is Electricity?
Contents
Electricity is like a powerful river that flows through conductors, such as wires and circuits, carrying energy that powers our world. The flow of electricity is measured in units called amperes, or amps for short. One ampere is equal to the flow of one coulomb of charge per second.
To understand how much power a device, like an LED light bulb, draws, it’s essential to know the difference between alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC). AC changes direction periodically, while DC flows in one direction only. Most homes and buildings use AC electricity, while DC is commonly used in batteries and electronic devices.
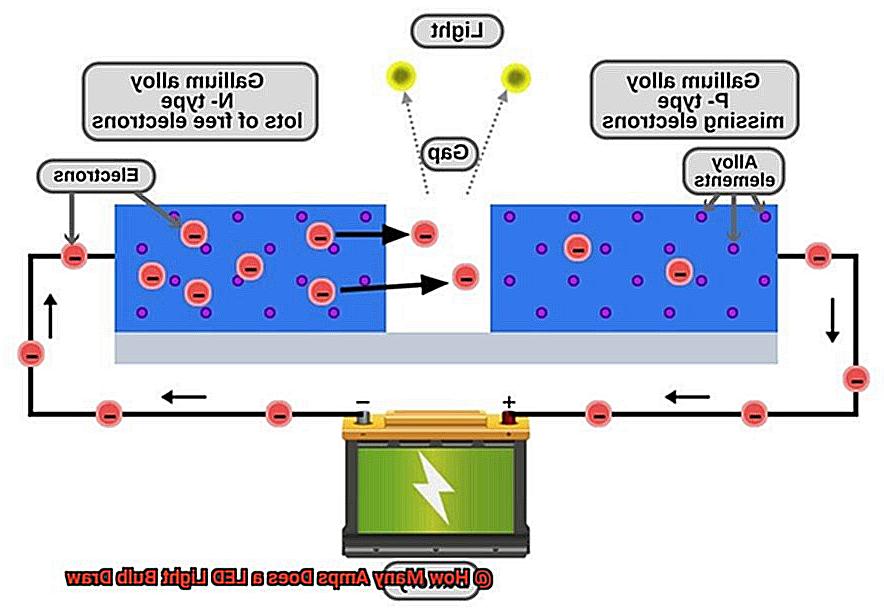
Electricity can be produced in various ways, including fossil fuels, nuclear energy, and renewable sources such as solar and wind power. However, regardless of the source, the flow of electricity is always a result of the movement of electrons through a conductor.
Now let’s talk about LEDs specifically. LED bulbs are known for their low current draw, which refers to the amount of electricity the bulb uses. Unlike traditional incandescent bulbs that draw up to 1 ampere of current, LED bulbs typically draw only 0.01-0.2 amps.
So how do LEDs use electricity? It all comes down to resistance and voltage. Resistance is like a speed bump in the flow of current, while voltage is like a push that helps the current flow. LED bulbs are designed to have low resistance and require very little voltage to work efficiently.
LEDs are a great choice if you want to save on energy costs and reduce your carbon footprint. They offer an environmentally friendly lighting solution for any space with their low current draw and long lifespan.
However, it’s important to check the manufacturer’s specifications for accurate information on wattage and voltage of a specific LED bulb.
How Much Current Does an LED Light Bulb Draw?
LED light bulbs are a marvel of modern technology, renowned for their energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness. But have you ever wondered how much current an LED bulb draws? Well, wonder no more because we’ve got the answers you need.
LED bulbs draw very little current, typically ranging between 10mA and 50mA. This is significantly lower than the current draw of traditional incandescent bulbs, which can suck up as much as 1A of current. In other words, LED bulbs are like a refreshing sip of lemonade on a hot summer day compared to the raging torrent of a waterfall.
The amount of current drawn by an LED bulb is determined by its wattage and voltage rating. For instance, a 5-watt LED bulb with a voltage rating of 120V will draw about 42mA of current. Similarly, a 10-watt LED bulb with a voltage rating of 240V will also draw roughly 42mA of current. It’s important to note that regardless of the voltage rating, the current drawn by an LED bulb remains constant.
The low current draw of LED bulbs makes them perfect for use in areas with limited power supply or where energy conservation is a priority. Additionally, since LED bulbs generate minimal heat compared to incandescent bulbs, they also reduce the risk of fire hazards.
In conclusion, when selecting an LED light bulb, it’s crucial to consider its wattage and voltage rating to ensure it meets your specific lighting needs.
By opting for an LED bulb with a low current draw, you’ll enjoy all the benefits of energy efficiency, cost-effectiveness and environmental sustainability while keeping your loved ones safe from fire hazards.
Factors Affecting the Current Draw of an LED Light Bulb
LED light bulbs are a shining example of energy efficiency, drawing less power than traditional incandescent bulbs. However, the current draw of an LED bulb can vary depending on several factors. To help you understand the key factors affecting current draw, we’ve compiled this list:
Firstly, wattage is a measure of a bulb’s power consumption. Higher wattage means more current drawn, but LED bulbs are designed to be more efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs. Even if you choose a high-wattage LED bulb, it will still consume less power than a lower-wattage incandescent bulb. It’s like comparing a marathon runner to a sprinter.
Secondly, voltage is important for LED bulbs. Most are designed to operate at a specific voltage, usually 120 volts in the US. If the voltage supplied is too high or too low, it can cause the bulb to draw more or less current than it should. It’s like baking a cake: too much or too little flour will ruin the recipe.
Thirdly, temperature affects an LED bulb’s current draw. LEDs generate heat when they’re in use, and if the temperature gets too high, it can cause the LED to draw more current than it should. This can lead to premature failure of the bulb. Think of it as running a marathon in scorching heat – you’ll tire out faster and not perform as well.
Fourthly, the driver regulates the amount of power supplied to the LED bulb. An efficient driver supplies power more precisely, which reduces the amount of current that the bulb draws. It’s like having a coach who understands your strengths and weaknesses and trains you accordingly.
Finally, dimming affects current draw. If an LED bulb is dimmable, its current draw changes at different brightness levels. As brightness decreases, so does current draw – just like decreasing volume on your stereo.
Benefits of Using LED Light Bulbs
Imagine never having to worry about constantly replacing light bulbs again. What if you could save money on your energy bill while also enjoying superior lighting quality? The solution is simple – switch to LED light bulbs. As an expert in this field, I can confidently say that LED bulbs offer a plethora of benefits that make them a smart choice for any household or commercial setting.
Let’s start with energy efficiency, which is one of the most significant advantages of using LED light bulbs. Unlike traditional incandescent bulbs, LED bulbs use significantly less energy, resulting in cost savings over time. In fact, a 60-watt LED bulb uses only 9 watts of energy. It’s like having a marathon runner in your home – they’re designed to use less energy and go the distance.
Another benefit of using LED bulbs is their long lifespan. These bulbs last up to 25 times longer than incandescent bulbs, which means you won’t have to replace them as frequently. This not only saves you money on replacements but also reduces waste. It’s like having a reliable companion by your side who never lets you down.
LED bulbs are also highly durable and resistant to shock and vibration. They are perfect for use in environments where traditional bulbs might break or shatter, such as industrial or outdoor settings. Think of them as a tough football player who can take a hit and keep going.
In addition to being durable, LED bulbs are environmentally friendly. They use less energy and contain no hazardous materials, making them safer for both people and the planet. Plus, they’re fully recyclable at the end of their lifespan. It’s like having a responsible citizen in your home – they care about the environment and do their part to reduce waste.
Lastly, LED bulbs provide improved lighting quality compared to traditional bulbs. They produce bright, natural-looking light that is easy on the eyes and does not flicker or hum like some other types of lighting. It’s like having a personal lighting coach who understands your strengths and weaknesses.
GXQW8ctNo0g” >
Conclusion
In conclusion, LED light bulbs are a revolutionary advancement in lighting technology. They are not only energy-efficient and cost-effective, but also eco-friendly. Unlike traditional incandescent bulbs that waste energy generating heat, LEDs use less power to produce brighter light. The amperage of an LED bulb varies based on its wattage and voltage rating.
LED bulbs draw very little current, typically ranging between 10mA and 50mA. This is significantly lower than the current draw of traditional incandescent bulbs, which can consume as much as 1A of current. With their low current draw, LED bulbs are ideal for areas with limited power supply or where energy conservation is a priority.
When choosing an LED light bulb, it’s important to consider its wattage and voltage rating to ensure it meets your specific lighting needs. Opting for an LED bulb with a low current draw will provide you with all the benefits of energy efficiency, cost-effectiveness and environmental sustainability while keeping your loved ones safe from fire hazards.
Apart from their low current draw, LED bulbs have several other advantages such as long lifespan, durability, improved lighting quality and being environmentally friendly. By switching to LED lighting, you’ll not only save money but also contribute towards protecting the environment.