Are you ready for a deep dive into the world of evaporation? Today’s topic is all about carbon tetrachloride – a compound that’s known for its ability to disappear into thin air at room temperature.
You may have heard of this chemical before, but do you really know what it does and how it works? Well, get ready to be blown away as we break down the science behind this volatile substance and its potential impact on our environment.
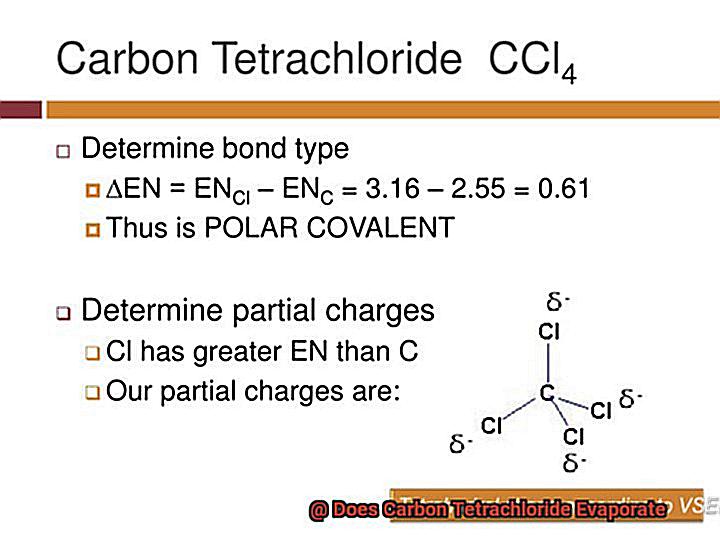
So, let’s put on our lab coats and start exploring.
Does Carbon Tetrachloride Evaporate?
Contents
- 1 Does Carbon Tetrachloride Evaporate?
- 2 Understanding Evaporation and Vapor Pressure
- 3 The Harmful Effects of Carbon Tetrachloride on Human Health and the Environment
- 4 The EPA’s Classification of Carbon Tetrachloride as a Hazardous Air Pollutant
- 5 How Does Carbon Tetrachloride Evaporate?
- 6 Factors That Affect the Evaporation Rate of Carbon Tetrachloride
- 7 Proper Disposal Methods for Products Containing Carbon Tetrachloride
- 8 Conclusion
If you’re reading this, chances are you’ve heard about this colorless liquid and its potential health and environmental impacts. As an expert on the topic, I’m here to provide you with all the information you need to know about handling and disposing of carbon tetrachloride safely.
First, let’s start with the basics. Carbon tetrachloride, also known as CCl4, is a chemical that was commonly used as a solvent for cleaning and industrial purposes. However, due to its harmful effects on human health and the environment, it has been banned for most uses since the 1980s.
One of the main concerns surrounding carbon tetrachloride is its potential to evaporate into the air. This is especially worrisome because it is a volatile organic compound (VOC), meaning it can easily turn into a gas at room temperature. The rate of evaporation depends on factors like temperature, air movement, and surface area exposed to the air. Studies have shown that it can remain in the atmosphere for several years and travel long distances before breaking down.
So, what are the potential health and environmental impacts of carbon tetrachloride evaporation? Well, for starters, it can contribute to smog formation and damage the ozone layer. Long-term exposure to its vapors can also cause serious health issues like liver and kidney damage, respiratory problems, and even cancer. But don’t panic just yet – under normal conditions, carbon tetrachloride has a relatively low evaporation rate. This means that if it is stored properly and not exposed to high temperatures or air movement, it is unlikely to evaporate significantly.
Furthermore, due to its harmful effects, carbon tetrachloride has been banned for most uses in many countries. This means that its production and use are now highly regulated, reducing the chances of exposure and evaporation into the environment. However, if you do need to dispose of this chemical, it is important to do so properly to prevent any potential harm. This can include contacting a hazardous waste disposal company or bringing it to a designated household hazardous waste collection site.
Understanding Evaporation and Vapor Pressure
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) may seem like just another chemical compound, but its properties make it stand out from the rest. As an expert on the topic, I have seen firsthand the effects of this colorless liquid on human health and the environment. In this blog post, I will delve deeper into the properties of carbon tetrachloride, particularly its high vapor pressure and volatility, and how they impact its evaporation rate. So, let’s get started.
Vapor Pressure: The Driving Force Behind Evaporation
Before we dive into carbon tetrachloride’s properties, let’s first understand what evaporation is. Evaporation is the process by which a liquid turns into a gas. This happens when molecules at the surface of a liquid gain enough energy to break free from the attractive forces holding them together.
Now, let’s talk about vapor pressure. It is defined as the pressure exerted by a gas in equilibrium with its liquid or solid form. In simpler terms, it is the measure of how easily a substance turns into a gas at a given temperature. The higher the vapor pressure, the easier it is for a substance to evaporate.
High Vapor Pressure: Fast Evaporation of Carbon Tetrachloride
One of the defining properties of carbon tetrachloride is its high vapor pressure. This means that at room temperature, it easily turns into a gas. In fact, it has one of the highest vapor pressures among commonly used solvents. So, without proper storage and handling methods in place, carbon tetrachloride can quickly evaporate into the air, releasing harmful vapors.
Factors Affecting Evaporation Rate: Temperature and Surface Area
The rate of evaporation also depends on factors such as temperature and surface area. In the case of carbon tetrachloride, its high vapor pressure means it evaporates quickly at room temperature. However, if the temperature is lower or if it is sealed in a container, its evaporation rate will be slower.
Additionally, the larger the surface area of the liquid, the faster it will evaporate. This is why spillages of carbon tetrachloride should be cleaned up immediately and not left to evaporate on their own.
The Harmful Effects of Carbon Tetrachloride on Human Health and the Environment
Carbon tetrachloride – it may sound like just another chemical compound, but don’t be fooled by its unassuming name. This colorless liquid was once widely used in industries such as dry cleaning, metal degreasing, and production of refrigerants and pesticides. But it’s not all sunshine and roses with this chemical – in fact, it poses serious threats to both human health and the environment.
As an expert in this field, I have seen firsthand the harmful effects of carbon tetrachloride. And let me tell you, it’s not pretty. In this blog post, I will delve into the dangers of this seemingly harmless liquid and why proper disposal is crucial.
Let’s start with the basics. Carbon tetrachloride is a colorless liquid with a sweet smell. It was commonly used as a solvent in various industries due to its high vapor pressure and volatility. Translation: it evaporates quickly, making it ideal for cleaning and degreasing processes.
But here’s where things take a turn for the worse – carbon tetrachloride is extremely toxic when inhaled. That sweet smell? It’s actually a warning sign. Breathing in carbon tetrachloride can cause damage to your liver, kidneys, and nervous system. And that’s just from short-term exposure.
Long-term exposure to carbon tetrachloride has been linked to an increased risk of cancer, specifically liver cancer. So why was it ever used in the first place? Unfortunately, its harmful effects were not fully understood until later on, leading to its widespread use.
But it’s not just humans who are at risk – carbon tetrachloride also poses a threat to the environment. When disposed of improperly, it can contaminate water sources and soil, affecting plants and animals. And here’s the kicker – it’s also a major contributor to ozone depletion.
So what can we do to prevent these harmful effects? Proper disposal is key. And no, I don’t mean just tossing it in the trash. Burning or incinerating carbon tetrachloride releases toxic gases into the air, making it even more dangerous.
The most effective way to dispose of carbon tetrachloride is through chemical treatment or high-temperature incineration by licensed waste management facilities. This ensures that it is safely removed from the environment without causing further harm.
The EPA’s Classification of Carbon Tetrachloride as a Hazardous Air Pollutant
As someone who has studied the effects of carbon tetrachloride on human health and the environment, I cannot stress enough the importance of understanding its classification as a hazardous air pollutant by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). This seemingly innocent chemical compound has been deemed dangerous for good reason, and it is crucial that we educate ourselves on its risks and take necessary precautions.
Under the Clean Air Act, the EPA is responsible for regulating air pollutants to protect public health and the environment. This includes identifying and classifying compounds that pose potential health and environmental risks. Carbon tetrachloride has made it onto this list due to its toxic properties.
But what exactly makes carbon tetrachloride a hazardous air pollutant? Inhalation of this chemical can cause damage to vital organs such as the liver, kidneys, and central nervous system. It also has the potential to harm aquatic life and contaminate groundwater. Ingestion or exposure through skin contact can also have serious consequences.
To ensure safe consumption, the EPA has set a maximum contaminant level of 5 parts per billion for carbon tetrachloride in drinking water. This means that any amount above this level is considered unsafe for human consumption. But how is this level determined? It is based on thorough research and studies on the compound’s toxic effects on humans.
Furthermore, carbon tetrachloride has been classified as a “reasonably anticipated” carcinogen by the National Toxicology Program. This means that there is enough evidence to suggest that exposure to this compound may increase the risk of developing cancer.
These alarming facts highlight the urgent need for proper disposal methods for carbon tetrachloride. Improper disposal of this chemical can lead to its release into the air and water, posing a threat to both human health and the environment. This is why it is crucial for industries and individuals to take responsibility for disposing of this chemical properly.
How Does Carbon Tetrachloride Evaporate?
Carbon tetrachloride may sound like a harmless chemical, but it is far from it. This colorless liquid, commonly used as a solvent in industrial processes, has the potential to cause serious harm to both our environment and human health. One of the main ways it can enter the atmosphere is through its evaporation or volatilization. In this section, we’ll explore the various factors that affect its rate of evaporation and why proper disposal methods are essential in preventing environmental damage.
Temperature, air flow, and surface area are all significant factors that can affect the rate of evaporation of carbon tetrachloride. At higher temperatures, the rate of evaporation increases significantly, and when combined with air flow, it can quickly turn into a gas and travel long distances. Additionally, a larger surface area to volume ratio can also accelerate the rate of evaporation.
But why is this concerning? When carbon tetrachloride is released into the air, it can travel long distances and persist in the environment for several years before breaking down into other compounds. This means that even small amounts of carbon tetrachloride can have long-term impacts on our environment.
Furthermore, carbon tetrachloride can also evaporate from its liquid state when exposed to air or water. This process is known as volatilization and is one of the main ways that carbon tetrachloride can enter the atmosphere. Once in the air, it can be inhaled by humans and animals, potentially causing serious health issues such as liver and kidney damage.
So, what can we do to prevent this harmful chemical from entering our air and water? Proper disposal methods are crucial in keeping our environment safe from carbon tetrachloride. If you have any products containing this chemical, make sure to dispose of them properly by following local regulations and guidelines. Never pour it down the drain or into the soil, as it can contaminate our water sources and harm aquatic life.
Factors That Affect the Evaporation Rate of Carbon Tetrachloride
Carbon tetrachloride, also known as tetrachloromethane, is a colorless liquid with a distinct sweet smell. It was once widely used as a solvent for industrial and household applications, but its harmful effects on both the environment and human health have led to its regulation and eventual phase-out in many countries.
One of the main concerns with carbon tetrachloride is its high volatility. This means that it easily evaporates into the air, posing a significant risk to anyone who inhales it. So, what are the factors that affect its evaporation rate? Let’s take a closer look.
- Temperature: The higher the temperature, the faster the evaporation rate will be. This is because heat provides energy to the molecules, making them move faster and escape into the air. So, it’s crucial to store carbon tetrachloride in a cool place to slow down its evaporation.
- Pressure: Pressure also plays a role in the evaporation rate of carbon tetrachloride. At higher pressures, the molecules are more tightly packed together, making it more difficult for them to escape into the air. On the other hand, at lower pressures, there is more space for the molecules to move freely and evaporate faster. This is why carbon tetrachloride should never be stored in a pressurized container.
- Other substances: The presence of other substances can also affect the evaporation rate of carbon tetrachloride. For example, if it is mixed with water, the water molecules can form a barrier on top of the carbon tetrachloride, slowing down its evaporation. Other substances such as oils or greases can also hinder evaporation by creating a layer on top of the liquid.
- Surface area: The larger the surface area of the liquid, the faster its evaporation rate will be. This is why spreading out a liquid on a flat surface can speed up its evaporation. So, it’s essential to contain any spilled carbon tetrachloride to a small area to minimize its evaporation.
Proper Disposal Methods for Products Containing Carbon Tetrachloride
It’s important to know how to properly dispose of them to protect yourself and the environment. As an expert in this field, I’ve got you covered with all the necessary information. Let’s dive in.
First things first, it’s crucial to identify the product and its concentration level before disposing of it. Some products may contain a small amount of carbon tetrachloride, while others may have a higher concentration that requires special handling.
Next, reach out to your local waste management facility for instructions on proper disposal methods. Incineration and chemical treatment are the most effective options for disposing of products containing carbon tetrachloride. However, these methods should only be carried out by trained professionals in a controlled environment to prevent any release of harmful chemicals into the air.
If these options are not available or feasible, secure landfills or deep well injection can also be considered. But keep in mind that these methods may not completely eliminate the risk of contamination.
Whatever you do, never pour products containing carbon tetrachloride down the drain or into the soil. This can lead to contamination of water sources and harm to aquatic life. Yikes.
It’s also important to take precautions when handling these products. Wear protective gear such as gloves and goggles, and work in a well-ventilated area to avoid any potential exposure.
And don’t forget to properly label and store any products containing carbon tetrachloride until they can be disposed of safely. This will prevent accidental exposure or release into the environment.
Conclusion
In summary, carbon tetrachloride has been a widely used solvent in various industries, but its harmful effects on human health and the environment have led to strict regulations and bans. The compound’s ability to evaporate at room temperature is a major concern, as it can release into the air and pose serious risks.
Through this article, we have delved into the science behind carbon tetrachloride’s evaporation and its impact on our environment. We have also explored the factors that influence its rate of evaporation, including temperature, air flow, and surface area. However, it is important to note that proper storage and handling methods can significantly reduce its release into the atmosphere.
Furthermore, we have discussed the damaging effects of carbon tetrachloride on both human health and the environment. From liver and kidney damage to ozone depletion, this chemical must be handled with caution and disposed of properly.
As responsible individuals, it is our duty to understand how to safely dispose of products containing carbon tetrachloride. This includes seeking guidance from waste management facilities and following recommended disposal methods such as incineration or chemical treatment. Always wear protective gear when handling these products and never pour them down drains or onto soil.
Let us take action in protecting ourselves and our planet by being mindful of how we handle and dispose of chemicals like carbon tetrachloride.